Intermittent Fasting: A Scientific Approach to Fat Loss or a Health Trap?
Intermittent fasting (IF) has become one of the most popular trends in the world of fitness and dieting. With promises of quick weight loss, improved metabolic health, and even longevity benefits, it’s no surprise that people are jumping on the bandwagon. But is intermittent fasting really the miracle solution it’s made out to be, or could it be a health trap in disguise? Let’s take a deeper look at what science says about this popular diet trend.

What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. Rather than focusing on what foods to eat, it’s more about when to eat. There are several methods, but the most popular include:
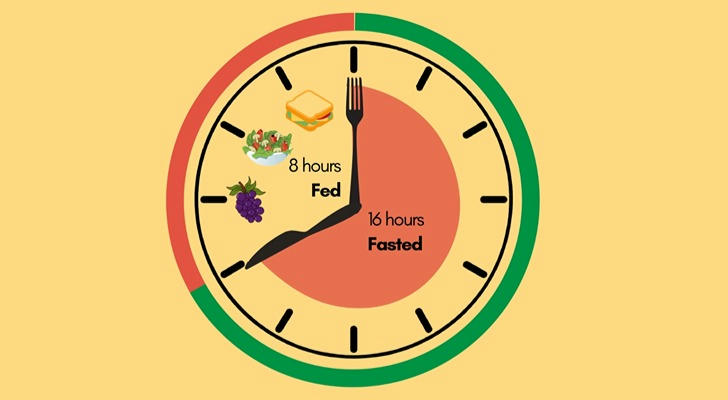
● 16/8 method: Fast for 16 hours, eat during an 8-hour window (e.g., 12 pm to 8 pm).

● 5:2 method: Eat normally for 5 days of the week, and restrict calorie intake (around 500-600 calories) on the other 2 days.
● Eat-Stop-Eat: 24-hour fasts once or twice a week.
While IF has gained popularity, it’s important to understand how it works, its benefits, and potential risks.
The Science Behind Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting affects the body in various ways. During the fasting periods, your body shifts from burning glucose (sugar) for energy to burning fat. This shift can help reduce body fat, which is why intermittent fasting is often associated with weight loss.
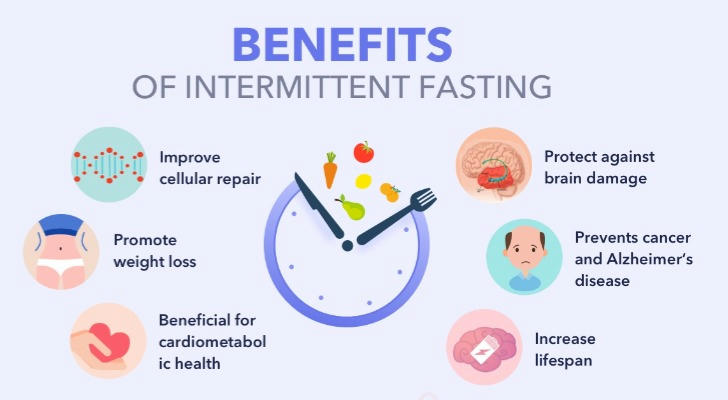
1. Boosts Fat Burning
Studies show that fasting increases the body’s ability to burn fat. When you fast, your insulin levels drop significantly, which helps your body use stored fat as energy. A study published in Obesity Reviews found that intermittent fasting can reduce body fat percentage and improve fat distribution in the body.
In fact, one study found that individuals who followed an intermittent fasting regimen saw an average fat loss of around 3-8% over 3-12 weeks, with no significant muscle loss. That’s a promising result for those looking to lose weight in a sustainable way.
2. Improves Insulin Sensitivity
One of the key benefits of intermittent fasting is its positive effect on insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance is a condition where the body doesn’t respond to insulin properly, leading to higher blood sugar levels and an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation found that intermittent fasting improved insulin sensitivity in both overweight and normal-weight individuals. By improving insulin sensitivity, intermittent fasting helps your body better manage blood sugar levels, which is crucial for overall health.
3. Promotes Longevity
Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may even have anti-aging effects. Research done on animals has shown that fasting can increase lifespan by reducing oxidative stress and promoting cellular repair processes. While more human studies are needed, some experts believe that intermittent fasting may help increase longevity and reduce age-related diseases.
Potential Risks of Intermittent Fasting
Despite the benefits, intermittent fasting is not without its risks. While it may work well for some, it could be problematic for others, especially if it’s not done correctly or if it doesn’t fit with one's lifestyle.
1. Nutrient Deficiency
One of the biggest risks associated with intermittent fasting is the potential for nutrient deficiencies. If you are fasting for extended periods, you may find it challenging to get all the vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients your body needs to stay healthy. This is especially true if you’re not eating balanced meals during your eating windows.
For instance, the 16/8 method restricts eating to an 8-hour window, which could lead to inadequate calorie intake or poor nutritional choices, especially if you’re consuming processed foods during the eating periods. A lack of proper nutrition can lead to fatigue, weakened immunity, and other health issues.
2. Disordered Eating Habits

For some individuals, intermittent fasting can trigger unhealthy relationships with food. Constantly restricting food intake may lead to binge eating during the eating window, which can result in weight gain rather than loss. It’s crucial to listen to your body and avoid extreme fasting, as this can lead to feelings of deprivation and create an unhealthy cycle.
3. Potential Impact on Mental Health
Fasting, particularly for extended periods, can lead to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. This is because the body may not be getting the necessary nutrients it needs to function optimally. One study found that fasting for extended periods can increase cortisol levels (the stress hormone), which may negatively affect mental well-being.
Is Intermittent Fasting Right for You?

So, is intermittent fasting a science-backed method for fat loss, or is it a health trap? The answer is: it depends. Intermittent fasting has shown to be effective for many individuals in terms of fat loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and metabolic health. However, it’s not suitable for everyone. If you have a history of eating disorders, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or have certain medical conditions, fasting may not be the best approach for you.
Before jumping into any fasting routine, it’s important to consider your lifestyle, health goals, and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health issues.
Practical Tips for Intermittent Fasting
If you decide to give intermittent fasting a try, here are some tips to ensure it’s done safely and effectively:
● Start Slowly: If you’re new to fasting, start with shorter fasting periods, such as 12 hours, and gradually increase the fasting window.
● Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods: During your eating window, prioritize whole foods like vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats to ensure you’re getting the nutrients your body needs.
● Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water, herbal teas, or black coffee to stay hydrated during fasting periods.
● Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body reacts during fasting. If you feel lightheaded, overly fatigued, or experience negative side effects, it’s essential to reassess your fasting plan.
Conclusion: Is Intermittent Fasting a Health Trap?
Intermittent fasting is a powerful tool for those seeking to lose fat, improve metabolic health, and potentially extend lifespan. However, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. While it can work wonders for some people, it may not be suitable for everyone. As with any diet or lifestyle change, it’s important to evaluate your personal goals and health conditions before committing to a fasting routine.
Ultimately, the key is balance. If done correctly, intermittent fasting can be a sustainable and effective method for improving health. But if done poorly, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies, disordered eating, and potential mental health struggles. Be mindful of how your body responds and choose a fasting approach that works best for you.
